How AI Risk Governance Builds Confidence and Accountability in AI Decisions
Turning the complexity of AI into clarity and confidence through AI Risk Governance, so decisions are smarter, risks are managed, and innovation moves forward with purpose.
AI is transforming how organizations make decisions, interact with customers, and manage risk. Every era of innovation reshapes expectations of trust, and AI raises the stakes like never before. With algorithms at the heart of operations, the focus shifts from what AI can do to how it acts responsibly. Governance provides the structure that makes this possible, setting boundaries and embedding accountability at every step. But a framework alone is not enough; confidence in AI must be actively built.
True confidence comes from clarity and oversight. Clear decision paths, defined responsibilities, and timely intervention create the infrastructure of what we call AI Risk Governance. This allows organizations to innovate with assurance, aligning progress with accountability.
As organizations move from testing AI to embedding it across operations, conversations shift from capability to consequence. Oversight becomes a tool, not a limit. It transforms speed into strategy and innovation into trust, ensuring growth happens with purpose and reliability.
Why Traditional Risk Management Falls Short in AI Environments
Conventional risk management was built for systems that stay the same. You mapped a process, added controls, and monitored for exceptions. The system you reviewed in January would likely behave the same way in December. This stability made oversight predictable and manageable.
AI changes that equation. Machine learning models adjust based on the data they see. Algorithms find new ways to optimize, even beyond the original design. A model that performs well in testing can behave differently once deployed. The code may stay the same, but the risks shift in ways traditional frameworks cannot catch.
That shift is magnified by volume and speed. AI systems make thousands of decisions daily across lending, hiring, and customer service. Each action might seem fine on its own, but patterns such as bias, drift, or inconsistency can form quickly, often unnoticed by conventional reviews. Quarterly checks arrive too late to prevent months of impact on customers, markets, and compliance.
Across industries, the challenge is the same. AI evolves in ways its creators cannot fully predict. Legacy tools were not built for this reality. To address these gaps, organizations need governance that starts with understanding how intelligent systems behave. Not how traditional systems used to work.
What Effective AI Risk Governance Looks Like
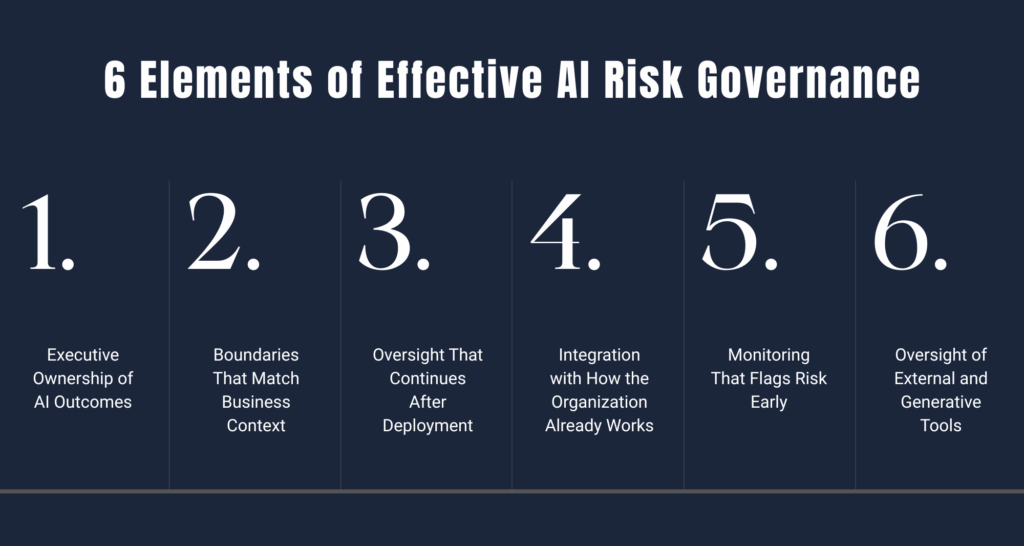
Once organizations recognize that traditional oversight cannot keep pace with AI, the next step is building governance that fits. Here are six strategic elements that help organizations move from awareness to action:
1. Executive Ownership of AI Outcomes
AI systems involve many teams, including data scientists, engineers, product leads, and business units. But when results affect customers, markets, or compliance, accountability must be clear. Governance starts at the top. Executive leaders take ownership of how systems behave, what risks they carry, and whether they support business goals.
This responsibility includes vendor tools. Even when AI is sourced externally, the organization remains accountable. Procurement teams set standards, preserve the right to review, and monitor third-party systems over time. Clear executive ownership ensures consistent decisions and oversight across all AI initiatives.
2. Boundaries That Match Business Context
Effective governance defines where AI belongs and where human judgment remains essential. Organizations set specific boundaries that reflect real-world decisions, rather than relying on broad statements about innovation or caution.
A bank might automate small loan approvals but require manual review for commercial lending. A hospital might triage patient questions with AI but reserve diagnoses for licensed professionals. Boundaries evolve as regulations shift and business needs change, keeping AI use aligned with purpose.
3. Oversight That Continues After Deployment
AI systems adapt over time, so governance must extend beyond launch. Teams continuously track performance, fairness, and confidence. When models shift, clear processes guide retraining, adjustment, or retirement.
Business owners lead these decisions because they understand the stakes. Documentation captures what the model was built to do, how it was designed, and how it has been performing. Continuous oversight ensures AI behavior aligns with expectations over time.
4. Integration with How the Organization Already Works
Governance is most effective when it fits naturally into existing workflows. Leading teams embed AI oversight into risk, audit, and compliance reviews. This makes approvals, concern escalation, and alignment seamless.
When governance is built into planning and procurement, it becomes part of everyday operations rather than an extra layer. Integration ensures oversight is sustainable and actionable across the organization.
5. Monitoring That Flags Risk Early
Even with integrated processes, real-time signals are essential to catch issues before they grow. Teams track early indicators like drops in confidence, changes in data quality, or shifts in user behavior. They also monitor whether safeguards are working, such as override rates or bias checks.
Early-warning monitoring complements continuous oversight, enabling teams to act before small issues become significant problems.
6. Oversight of External and Generative Tools
AI increasingly comes from outside the organization, including embedded features, SaaS platforms, and generative systems that employees adopt informally. These tools can pose risks if not properly governed.
Organizations define approved tools, set data-sharing limits, and clarify how outputs should be checked. Vendor practices are vetted, contracts preserve review rights, and monitoring continues post-launch. Covering external tools ensures governance extends beyond internal systems to all AI influencing the organization.
Governance as a Strategic Advantage
Once governance is embedded across teams, its impact extends beyond operations. It becomes visible to customers, partners, regulators, and investors. That visibility turns oversight into a strategic signal, shaping perception, earning trust, and strengthening market position.
Organizations with clear governance move faster. Buyers request proof before signing contracts. Investors include oversight in ESG reviews and due diligence. Strong AI Risk Governance supports valuation, accelerates funding, and reduces friction in high-stakes decisions.
It also attracts talent. Skilled professionals look for teams that build systems with care. They stay where ethics are clear, accountability is real, and governance is part of the culture, not just a compliance layer.
Beyond culture and talent, early adopters gain something others cannot replicate: experience. They refine oversight through real cases, build credibility through action, and adapt quickly when regulations shift. That maturity becomes a competitive edge.
Governance is no longer a back-office concern. It is a front-line differentiator. The organizations that lead today will not only exceed standards, they will help define them.